
Breaking News
 Brighteon Broadcast News, Jan 7, 2026 - Doctors Replaced by AI...
Brighteon Broadcast News, Jan 7, 2026 - Doctors Replaced by AI...
 US Blockade Of Venezuela Triggers New Spike In Silver Price!
US Blockade Of Venezuela Triggers New Spike In Silver Price!
 Elon Musk Expects True AGI in 2026-2027 and Superintelligence About 2030...
Elon Musk Expects True AGI in 2026-2027 and Superintelligence About 2030...
 They Can't Stop The Unstoppable Rise Of Silver...
They Can't Stop The Unstoppable Rise Of Silver...
Top Tech News
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Repairing damaged cartilage with a man-made bio-glass
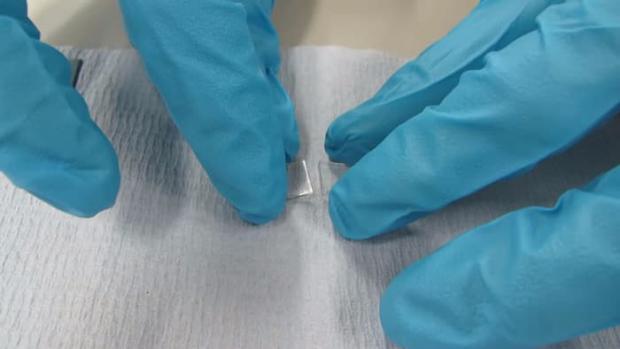
Cartilage, which is found in joints, as well as between vertebrae in the spine, is not as easy to repair as other types of connective tissue, and its degeneration can leave patients in a lot of pain. A new bio-material, made up of a mixture of a polymer called polycaprolactone and silica, could help with the ability to replace lost cartilage.
It's similar to real cartilage in that it's strong, flexible and durable, giving it the same load-bearing and shock-absorbing properties. Furthermore, it's possible to produce the material in a biodegradable ink form, allowing researchers to 3D print structures. The material also has self-healing properties, allowing two sections to firmly reattach after being pulled apart.
The researchers believe that the material could be useful in numerous situations. For example, it could be used to create implants for patients with damaged intervertebral discs, or to 3D print tiny biodegradable scaffolds that replicate lost cartilage in the knee.



