
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Liquid light switch bridges the gap between light and electricity
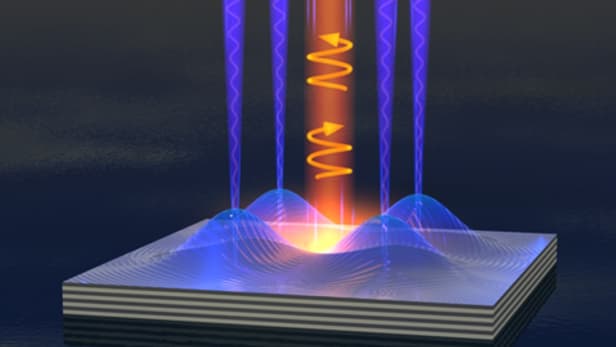
Scientists working at the University of Cambridge have used a form of liquid light to create a semiconductor switch that is so small that it not only blurs the distinction between light and electricity, but could also enable the development of much faster and smaller electronic components well into the future.
With the limits of Moore's Law looming closer day by day, the demand for faster, smaller electronics ever increasing, and microelectronics reaching the point where quantum effects are seriously challenging the continued use of electrons as a transporter of data, researchers the world over are exploring ways to solve these problems.
With contemporary methods used to convert between electrical signals and optical ones considered largely inefficient, University of Cambridge researchers believe that it would be better simply to cut out the middleman and mix the two together. In a quest to achieve this, the researchers created a switch using a new state of matter known as a Polariton Bose-Einstein condensate to combine electric and optical signals, while consuming infinitesimally small quantities of energy in the process.



