
Breaking News
 BANK OF AMERICA SURRENDERS: BofA Just Issued a $309 Silver Alert (Physical Premiums Exploding)
BANK OF AMERICA SURRENDERS: BofA Just Issued a $309 Silver Alert (Physical Premiums Exploding)
 Steve Witkoff says they are close to finishing "a prosperity agreement" for Ukraine,...
Steve Witkoff says they are close to finishing "a prosperity agreement" for Ukraine,...
 NOW - Starmer says a declaration of intent has been signed...
NOW - Starmer says a declaration of intent has been signed...
 Remarks at the New Jersey Bankers Association, Jersey City, New Jersey
Remarks at the New Jersey Bankers Association, Jersey City, New Jersey
Top Tech News
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Inductive heating of Magnetic Nanoparticles enables safe thawing of cryopreserved...
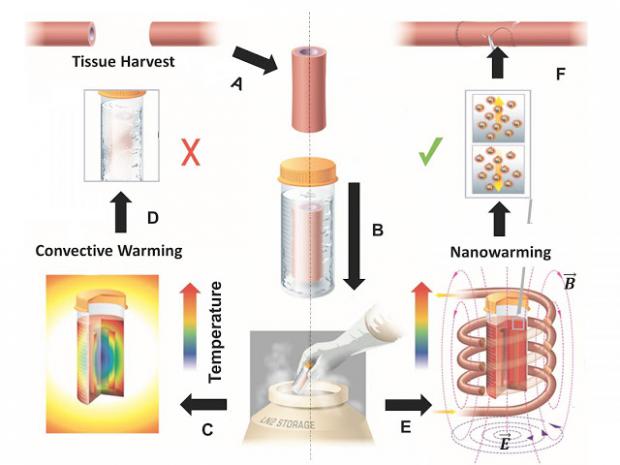
A new study reveals that nanotechnology can be used to rapidly rewarm cryogenically treated samples without damaging delicate frozen tissues, which may someday help make organ cryopreservation a reality. More than 60% of the hearts and lungs donated for transplantation must be discarded annually, because these tissues cannot be kept on ice for longer than four hours. According to recent estimates, if only half of unused organs were successfully transplanted, transplant waiting lists could be eliminated within two years. Long-term preservation methods like vitrification - which involves super-cooling biological samples to a glassy state - could establish tissue storage banks and reduce transplant rejection rates, greatly facilitating the process to find matching donors when needed.
* we have been able to vitrify organs since the 1980s but have not been able to safely thaw them
* we need to evenly and rapidly heat cryopreserved organs
* microwaving leaves hotspots that damage thawed organs
* magnetic nanoparticles enable the necessary rapid heating (100 degrees per minute) but without hotspots



