
Breaking News
 Alex Jones & Steve Bannon Warn, The ANTIFA-Sponsored Murder Of Charlie Kirk...
Alex Jones & Steve Bannon Warn, The ANTIFA-Sponsored Murder Of Charlie Kirk...
 Here's that fast vid President Trump posted, hinting at what he is about to do
Here's that fast vid President Trump posted, hinting at what he is about to do
 The 2 Billion View Video: Charlie Kirk's Most Viewed Clips of 2024
The 2 Billion View Video: Charlie Kirk's Most Viewed Clips of 2024
 Conservatives Are Being Targeted – Louder with Crowder CEO Warns / Redacted
Conservatives Are Being Targeted – Louder with Crowder CEO Warns / Redacted
Top Tech News
 Tesla Megapack Keynote LIVE - TESLA is Making Transformers !!
Tesla Megapack Keynote LIVE - TESLA is Making Transformers !!
 Methylene chloride (CH2Cl?) and acetone (C?H?O) create a powerful paint remover...
Methylene chloride (CH2Cl?) and acetone (C?H?O) create a powerful paint remover...
 Engineer Builds His Own X-Ray After Hospital Charges Him $69K
Engineer Builds His Own X-Ray After Hospital Charges Him $69K
 Researchers create 2D nanomaterials with up to nine metals for extreme conditions
Researchers create 2D nanomaterials with up to nine metals for extreme conditions
 The Evolution of Electric Motors: From Bulky to Lightweight, Efficient Powerhouses
The Evolution of Electric Motors: From Bulky to Lightweight, Efficient Powerhouses
 3D-Printing 'Glue Gun' Can Repair Bone Fractures During Surgery Filling-in the Gaps Around..
3D-Printing 'Glue Gun' Can Repair Bone Fractures During Surgery Filling-in the Gaps Around..
 Kevlar-like EV battery material dissolves after use to recycle itself
Kevlar-like EV battery material dissolves after use to recycle itself
 Laser connects plane and satellite in breakthrough air-to-space link
Laser connects plane and satellite in breakthrough air-to-space link
 Lucid Motors' World-Leading Electric Powertrain Breakdown with Emad Dlala and Eric Bach
Lucid Motors' World-Leading Electric Powertrain Breakdown with Emad Dlala and Eric Bach
 Murder, UFOs & Antigravity Tech -- What's Really Happening at Huntsville, Alabama's Space Po
Murder, UFOs & Antigravity Tech -- What's Really Happening at Huntsville, Alabama's Space Po
New ultrathin semiconductor materials exceed some of silicon's capabilities
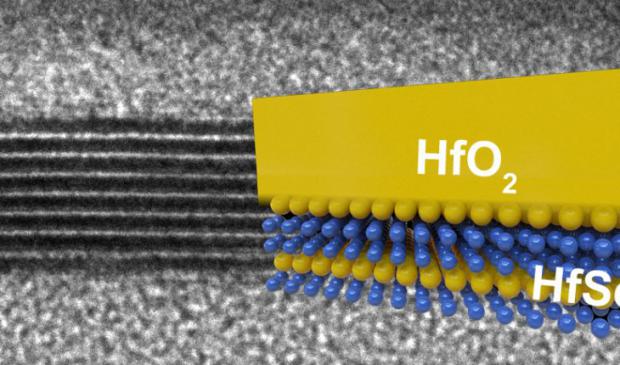
In this greatly enlarged cross-section of an experimental chip, the bands of black and white reveal alternating layers of hafnium diselenide – an ultrathin semiconductor material – and the hafnium dioxide insulator. The cross-section matches an overlaid color schematic on the right. (Image credit: Michal Mleczko)
The new materials can also be shrunk to functional circuits just three atoms thick and they require less energy than silicon circuits. Although still experimental, the researchers said the materials could be a step toward the kinds of thinner, more energy-efficient chips demanded by devices of the future.
Science Advances – HfSe2 and ZrSe2: Two-dimensional semiconductors with native high-κ oxides
Silicon's strengths
Silicon has several qualities that have led it to become the bedrock of electronics, Pop explained. One is that it is blessed with a very good "native" insulator, silicon dioxide or, in plain English, silicon rust. Exposing silicon to oxygen during manufacturing gives chip-makers an easy way to isolate their circuitry. Other semiconductors do not "rust" into good insulators when exposed to oxygen, so they must be layered with additional insulators, a step that introduces engineering challenges. Both of the diselenides the Stanford group tested formed this elusive, yet high-quality insulating rust layer when exposed to oxygen.



