
Breaking News
 Losing Chickens? Tools Needed for Trapping Poultry Predators
Losing Chickens? Tools Needed for Trapping Poultry Predators
 Metals Tell the Truth About the Economy
Metals Tell the Truth About the Economy
 RFK Jr. baffled over how Trump is alive with diet 'full of poison,'
RFK Jr. baffled over how Trump is alive with diet 'full of poison,'
 Dr. Peter McCullough Responds To Anthony Fauci Criminal Referral
Dr. Peter McCullough Responds To Anthony Fauci Criminal Referral
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
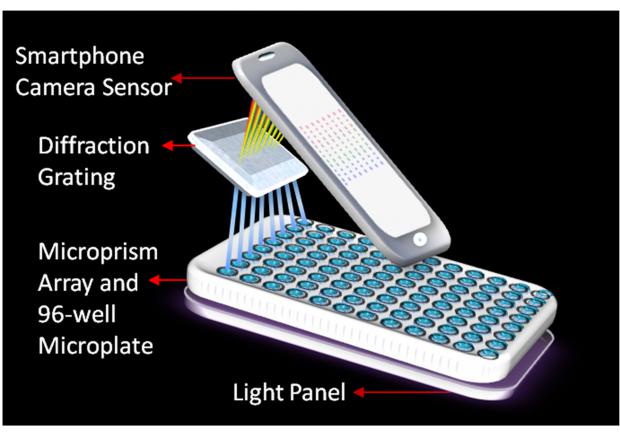
Diagnostic device uses smartphone to check almost 100 samples at once

 Programmed DNA nanorobots to shrink cancer tumors by cutting off their blood supplyProgrammed DNA nanorobots to shrink cancer tumors by cutting off their blood supply
Programmed DNA nanorobots to shrink cancer tumors by cutting off their blood supplyProgrammed DNA nanorobots to shrink cancer tumors by cutting off their blood supply Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

