
Breaking News
 Adobe in Action's Adobe Brickmaking Process
Adobe in Action's Adobe Brickmaking Process
U.S. Is Being Driven Out Of The Middle East, Iran Is Demolishing Israel, Hegseth Is A War Criminal
 Iran War Hits Cyber, Food, Energy: Stryker Cyberattack, India Fertilizer Stoppage
Iran War Hits Cyber, Food, Energy: Stryker Cyberattack, India Fertilizer Stoppage
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Crispr gene therapy fixes disease in a human embryo
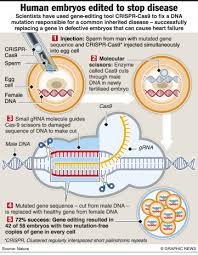
A single letter mistake in the gene for FBN1, which codes for the fibrillin protein, can cause a ripple effect of problems—from loose joints to weak vision to life-threatening tears in the heart's walls. Starting with healthy eggs and sperm donated by a Marfan syndrome patient, the team of researchers from Shanghai Tech University and Guangzhou Medical University used an IVF technique to make viable human embryos. Then they injected the embryos with a Crispr construct known as a base editor, which swaps out a single DNA nucleotide for another—in this case, removing an "A" and replacing it with a "G". They kept the embryos alive for another two days in the lab, long enough to run tests to see how well the editing worked. Sequencing revealed that all 18 embryos had been edited, with 16 of the embryos bearing only the corrected version of the FBN1 gene. In two of the embryos, additional unwanted edits had also taken place.

 Now Its Time to PANIC
Now Its Time to PANIC
 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

