
Breaking News
 Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
 Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
 The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
 Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Molecule produced during fasting has anti-aging effect on vascular system
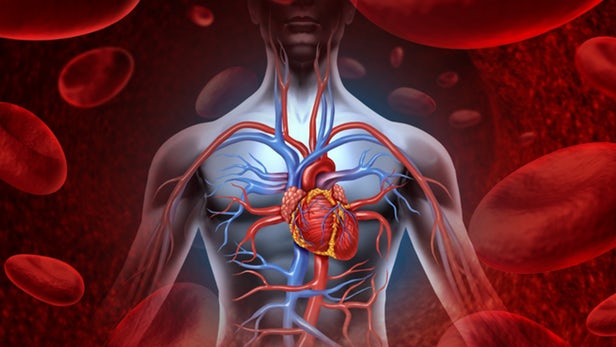
Diet trends like intermittent fasting and ketogenesis are proving wildly popular for their rapid weight-loss effects, but scientists are also starting to uncover how they might benefit the body in other, longer term ways. Case in point: a molecule produced during fasting has now been found to apply the brakes to aging of the vascular system, a process closely tied to the aging of the human body as a whole.
When the body enters ketosis, a metabolic state induced by fasting and low-carb diets, it turns to the body's stored fats for energy, rather than glucose. One of these sources of energy, known collectively as ketones, is a molecule called β-Hydroxybutyrate.
"Previously, studies on ketone bodies focused on energy metabolism, but this study showed that there are other physiological effects which regulate cell cycle to retardate aging progression," study senior author Dr. Ming-Hui Zou tells New Atlas.
One such earlier study, at Harvard University last year, demonstrated how fasting can alter the activity of mitochondrial networks inside our cells, leading to increased lifespan, slower aging and improved health.
Zou and his team at Georgia State University set out to explore how heightened β-Hydroxybutyrate levels might have similar effects by interfering with what are known as senescent cells, which are cells that are no longer able to multiply and divide.
The scientists found that β-Hydroxybutyrate puts the brakes on senescent vascular cells at just the right time, actively promoting cell division and preventing them from growing old. When injected into mice, it was also found to promote stem cell factors that protect against DNA-related senescence to keep blood vessels young.



