
Breaking News
 Electricity Demand Is Surging, The Grid Isn't Ready: IEA
Electricity Demand Is Surging, The Grid Isn't Ready: IEA
 Bibi Seeks US Muscular Action On Iran In Seventh Meeting With Trump
Bibi Seeks US Muscular Action On Iran In Seventh Meeting With Trump
 Duffy: FAA And Military "Acted Swiftly" To Combat "Cartel Drone Incursion" On US
Duffy: FAA And Military "Acted Swiftly" To Combat "Cartel Drone Incursion" On US
 A mom was ASSAULTED by a mob of students from @IssaquahSchools...
A mom was ASSAULTED by a mob of students from @IssaquahSchools...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Mars-bound CubeSats catch first glimpse of the Red Planet
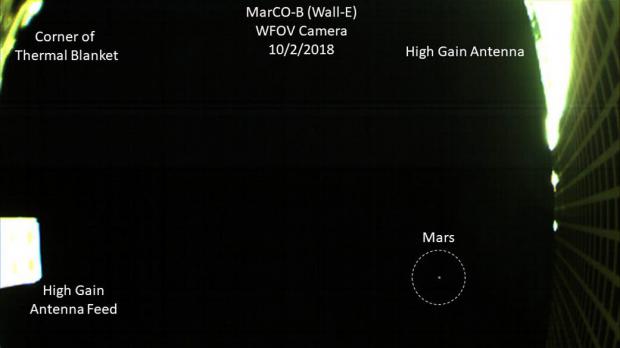
These two little spacecraft are the first of their kind to venture into deep space, and now they've sent us back a post card of their first glimpse of the Red Planet.
The image, snapped by MarCO-B on October 3, shows Mars as a tiny, pale red dot towards the right of frame, much like the "Pale Blue Dot" photo they sent as they whizzed away from Earth. To line up the shot, the CubeSat had to be programmed to rotate in space to point the wide-angle camera towards Mars.
A few onboard instruments photobomb the image too: part of a thermal blanket can be seen at the top left, and below that the antenna feed peeks in. The right-hand side of the image is framed by the high gain antenna.
The photo was taken from a distance of about 8 million miles (12.8 million km), but interestingly the journey to Mars will still involve another 53 million miles (85 million km) because the Red Planet is moving away from the CubeSats.
Once they arrive at Mars, the two MarCOs will help relay communications back to Earth as the InSight lander touches down. That said, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) will do most of the heavy lifting there – the MarCO mission is mostly a test to see if CubeSats are able to survive the rigors of space travel.



