
Breaking News
 Charlie's Killer Was MKUltra'd?
Charlie's Killer Was MKUltra'd?
 Doctors are finally admitting that biopsies Spread Cancer…
Doctors are finally admitting that biopsies Spread Cancer…
 We MUST keep talking about this, demand Voter ID. Joe Rogan and Elon Musk on Fraud
We MUST keep talking about this, demand Voter ID. Joe Rogan and Elon Musk on Fraud
 Nick Shirley exposes there are 1,200 medical transport companies in Minnesota.
Nick Shirley exposes there are 1,200 medical transport companies in Minnesota.
Top Tech News
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Unlikely drug pair combine to cut off cancer's energy supply
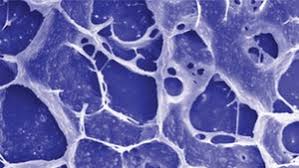
New research out of the University of Basel describes a drug cocktail that has the effect of putting this out of action, leading the cancer cells to wither and die instead.
Molecular scientists at the University of Basel actually discovered two years ago that a commonly used diabetes drug could be combined with a 50-year-old hypertension medication to inhibit tumor growth. Named metformin and syrosingopine, respectively, the scientists knew beforehand that the former had some anti-cancer properties, but only by mixing it with the latter did it seem to have any meaningful effect.
They have now carried out follow-up experiments in mice to better understand how this process slows cancer growth, and it centers on a molecule called NAD+ that is central to converting nutrients into energy. NAD+ is produced through two cellular pathways, one of which metformin was known to block. The other, it has now been found, can be shut down by syrosingopine's ability to cause bottlenecks in some very key areas.
"In order to keep the energy-generating machinery running, NAD+ must be continuously generated from NADH," explains Don Benjamin, first author of the study. "Interestingly, both metformin and syrosingopine prevent the regeneration of NAD+, but in two different ways."



