
Breaking News
 Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
Full-Out, Digitized Technocratic Rule Is Not Around The Corner, It Is Next Door
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
 Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Hormuz Is Closing -- Oil Skyrockets. Food and Chips Are Next...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Two new studies strengthen the gut-brain connection in autism
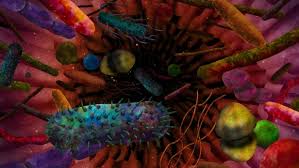
The new research reveals how gastrointestinal problems can be triggered by the same gene mutations associated with autism, and a striking mouse study has demonstrated how a fecal transplant from humans with autism can promote autism-like behaviors in the animals.
One of the more intriguing areas of microbiome research is the growing connection between gut bacteria and autism. Several recent, albeit small, studies have revealed behavioral and psychological symptoms of autism in children can be improved using fecal transplants from healthy subjects. Exactly how the microbiome could be influencing autism symptoms is still unclear but one new study, led by researchers from Caltech, has strengthened this intriguing gut-brain hypothesis.
The research began by taking microbiome samples from human subjects, both with and without autism, which were then transplanted into germ-free mice. The results were striking, with the animals receiving gut bacteria from human subjects with autism displaying hallmark autistic behaviors such as decreased social interactions and increased repetitive behaviors. The mice administered with gut bacteria from non-autistic human donors did not display these behavioral symptoms.

 Going Down with the Ship
Going Down with the Ship


