
Breaking News
 Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
 China Just Dropped a 6% TAX on Gold - The Market Wasn't Ready for This
China Just Dropped a 6% TAX on Gold - The Market Wasn't Ready for This
 Banks' Strategic Silver Market Manipulation During Off-Hours Trading
Banks' Strategic Silver Market Manipulation During Off-Hours Trading
 No new North Sea oil wells for first time since 1960
No new North Sea oil wells for first time since 1960
Top Tech News
 The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
 Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
 A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
 Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
Review: Thumb-sized thermal camera turns your phone into a smart tool
 Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
Army To Bring Nuclear Microreactors To Its Bases By 2028
 Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
Nissan Says It's On Track For Solid-State Batteries That Double EV Range By 2028
 Carbon based computers that run on iron
Carbon based computers that run on iron
 Russia flies strategic cruise missile propelled by a nuclear engine
Russia flies strategic cruise missile propelled by a nuclear engine
 100% Free AC & Heat from SOLAR! Airspool Mini Split AC from Santan Solar | Unboxing & Install
100% Free AC & Heat from SOLAR! Airspool Mini Split AC from Santan Solar | Unboxing & Install
 Engineers Discovered the Spectacular Secret to Making 17x Stronger Cement
Engineers Discovered the Spectacular Secret to Making 17x Stronger Cement
Laser-driven Particle Accelerator Made Ten Thousand Times Smaller
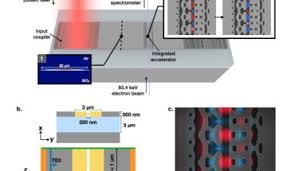
Current implementations of DLAs rely on free-space lasers directly incident on the accelerating structures, limiting the scalability and integrability of this technology. Researchers present the first experimental demonstration of a waveguide-integrated DLA, designed using a photonic inverse design approach. These on-chip devices accelerate sub-relativistic electrons of initial energy 83.4 keV by 1.21 keV over 30 µm, providing peak acceleration gradients of 40.3 MeV/m. This progress represents a significant step towards a completely integrated MeV-scale dielectric laser accelerator.
Dielectric laser accelerators have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional RF accelerators due to the large damage threshold of dielectric materials the commercial availability of powerful NIR femtosecond pulsed lasers, and the low-cost high-yield nanofabrication processes which produce them. Together, these advantages allow DLAs to make an impact in the development of applications such as tabletop free-electron-lasers, targeted cancer therapies, and compact imaging sources.



