
Breaking News
 Mike Benz just examined Epstein files and he's got a telltale theory…
Mike Benz just examined Epstein files and he's got a telltale theory…
 BREAKING GLOBAL EXCLUSIVE: Former High-Level CIA Operative Patrick Byrne Reveals That...
BREAKING GLOBAL EXCLUSIVE: Former High-Level CIA Operative Patrick Byrne Reveals That...
 Junk-food Bans for SNAP Users To Begin in January
Junk-food Bans for SNAP Users To Begin in January
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Technique Allows Kidney Transplants From Any Donor
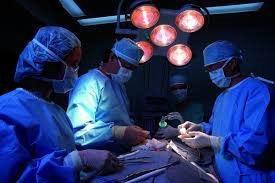
Every year, 4,500 Americans die waiting for a kidney transplant. It's not just because there aren't enough donors—part of the problem is that donors need to be compatible to prevent the recipient's body from rejecting the new kidney. They need the right blood type, but they also have to have the right combination of six antigens--molecules on a cell that have the capacity to trigger an immune response. Any two random people have a one in 100,000 chance that all six antigens will match, and even then it's not a guarantee that the kidney won't be rejected.
Fifteen years ago, researchers from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine started developing a technique to quiet the recipient's immune system, making even incompatible donors a match. Now, after an eight-year study and evaluating thousands of patients, they have proof that this immune-quieting method works better than the alternatives and is saving lives, which could make it more widespread. The researchers published a study today in the New England Journal of Medicine.

 The Ever-Widening War
The Ever-Widening War

