
Breaking News
 SILVER CRASHES TO $75 - But China Is Paying $89 (Ghost Week Trap)
SILVER CRASHES TO $75 - But China Is Paying $89 (Ghost Week Trap)
 Firegate: Democrat LA Mayor Karen Bass' Admin Altered Palisades Fire Report & Deleted Evidence
Firegate: Democrat LA Mayor Karen Bass' Admin Altered Palisades Fire Report & Deleted Evidence
 BREAKING: Candace Owens' Massive Mind Control House of Cards is Now Collapsing in Real Time
BREAKING: Candace Owens' Massive Mind Control House of Cards is Now Collapsing in Real Time
 We Cannot Build an Economy on Lies
We Cannot Build an Economy on Lies
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
The End Of Root Canals?
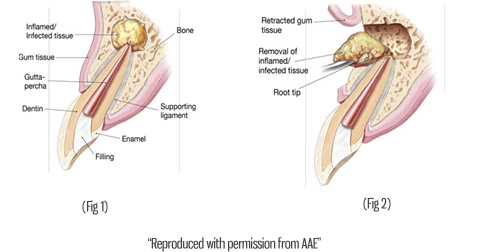
What if damaged teeth could heal themselves? That's the inspiration behind a new project from Harvard and the University of Nottingham to create stem cell stimulating fillings.
Dentists treat hundreds of millions of cavities each year by drilling out the decay and putting in a filling.
But 10 to 15 percent of those fillings fail, says Adam Celiz, a therapeutic biomaterials researcher from University of Nottingham. And that leads to millions of root canals to remove the tooth's pulp, the soft tissue in the center of the tooth that contains the blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. A root canal can weaken the tooth, which may eventually need to be pulled.
Celiz and his fellow researchers have developed a new kind of filling made from synthetic biomaterial that can stimulate the growth of stem cells in the pulp of the tooth. Just like regular fillings, the biomaterial is injected into the tooth and hardened with UV light.



