
Breaking News
 $100 Solar Panel vs $100 Wind Turbine in a Normal Backyard
$100 Solar Panel vs $100 Wind Turbine in a Normal Backyard
 Tucker Carlson on Iran War latest, Trump's MAGA collapse, & Israel's media blackout | Redact
Tucker Carlson on Iran War latest, Trump's MAGA collapse, & Israel's media blackout | Redact
 INDIANA DRAWS THE LINE ON FARMS
INDIANA DRAWS THE LINE ON FARMS
 $35,000 Solar System Cannot Charge to 100%?? Seriously Sol Ark and Deye?
$35,000 Solar System Cannot Charge to 100%?? Seriously Sol Ark and Deye?
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Self-contained prototype brings artificial photosynthesis a step closer to commercial reality
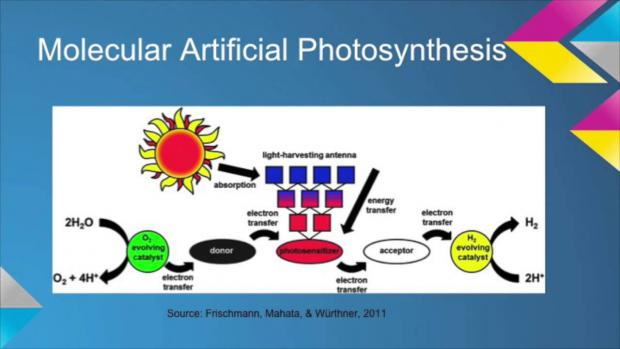
As part of the on-going pursuit of this goal, researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich claim to have created a working, compact, self-contained artificial photosynthesis system that could form the basis for practical commercial devices.
Photosynthesis in plants and certain types of algae is the process where light energy is transformed into chemical energy to synthesize simple carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. In artificial photosynthesis, or photoelectrochemical water splitting, solar energy is used to split hydrogen molecules from water (or even further refine it into methane in some systems).
In this latest system, as in most other artificial photosynthesis devices, the amalgamation of a solar cell and an electrolyzer is used to capture solar energy to split water into hydrogen. A technique employed since the 1970s, most research has concentrated on increasing efficiency by developing new absorber materials and catalysts.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

