
Breaking News
 Israel First Vs America First Conservatives
Israel First Vs America First Conservatives
 The COVID Vaccine DNA Bombshell They Tried to Hide | Exclusive with Dr. David Speicher
The COVID Vaccine DNA Bombshell They Tried to Hide | Exclusive with Dr. David Speicher
 Alarm Bells Going off EVERYWHERE, and Putin and China Smell Blood | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Alarm Bells Going off EVERYWHERE, and Putin and China Smell Blood | Redacted w Clayton Morris
 Ben Shapiro Joining CNN Exposes His REAL Scheme
Ben Shapiro Joining CNN Exposes His REAL Scheme
Top Tech News
 Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
 SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
 Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
 HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
 What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
 Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
Japan just injected artificial blood into a human. No blood type needed. No refrigeration.
 The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
The 6 Best LLM Tools To Run Models Locally
 Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
Testing My First Sodium-Ion Solar Battery
 A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
A man once paralyzed from the waist down now stands on his own, not with machines or wires,...
This Incredible Fabric Generates Electricity From Sunlight And Movement
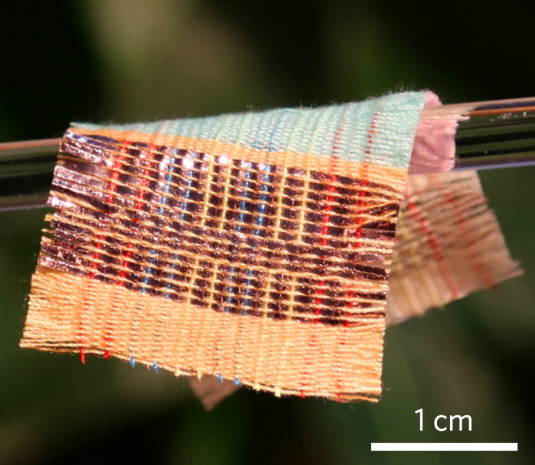
Every day, unique and eco-friendly innovations are unveiled. However, a textile designed by engineers with the Georgia Institute of Technology, Chongqing University, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences is likely one you missed hearing about. The fabric is newsworthy because it is capable of producing electricity from sunlight and fiction – including the wind. It could be a total game-changer, yet no one has really heard about it.
According to MotherBoard, the material is both breathable and robust and allows for enough motion to make it a good candidate for wearable electronics. In fact, an image below demonstrates a few of its uses, including powering wearable electronics and directly charging a cellphone.

Credit: Wang et al
The textile consists of solid photovoltaic elements woven together with copper electrodes. The material acts as triboelectric nanogenerator, meaning it is capable of converting certain frictional forces into electric charge, "a la static electricity."
Zhong Lin Wang from Georgia Tech explains:
"Here, we present a foldable and sustainable power source by fabricating an all-solid hybrid power textile with economically viable materials and scalable fabrication technologies. Based on lightweight and low-cost polymer fibres, the reported hybrid power textile introduces a new module fabrication strategy by weaving it in a staggered way on an industrial weaving machine via a shuttle-flying process."



