
Breaking News
 IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: December 28, 2025 Edition
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Inside the Race to Build the Battery of Tomorrow
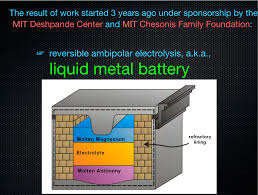
he lack of glamour is especially conspicuous on the lower floors of MIT's materials science department, where one lab devoted to building and testing the next world-changing energy storage device could easily be mistaken for a storage closet.
At the back of the cramped room, Donald Sadoway, a silver-haired electrochemist in a trim black-striped suit and expensive-looking shoes, rummages through a plastic tub of parts like a kid in search of a particular Lego. He sets a pair of objects on the table, each about the size and shape of a can of soup with all the inherent drama of a paperweight.
No wonder it's so hard to get anyone excited about batteries. But these paperweights—er, battery cells—could be the technology that revolutionizes our energy system.



