
Breaking News
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
 Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Embryo Breakthrough: Artificial Human Life Now Possible In Lab
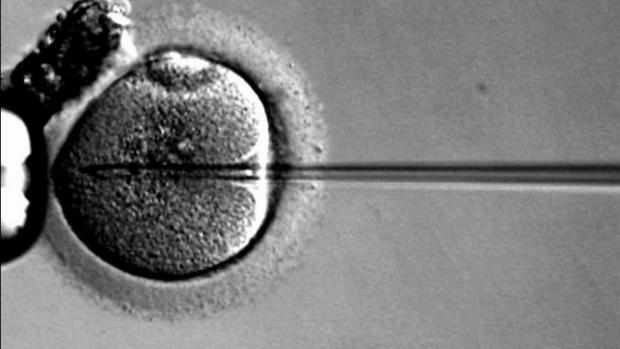
Cambridge University mixed two kinds of mouse stem cells and placed them on a 3D scaffold. After four days of growth in a tank of chemicals designed to mimic conditions inside the womb, the cells formed the structure of a living mouse embryo.
The breakthrough has been described as a 'masterpiece' in bioengineering, which could eventually allow scientists to grow artificial human embryos in the lab without the need for a sperm or an egg.
Growing embryos would help researchers to study the very early stages of human life so they could understand why so many pregnancies fail, but is likely to prove controversial and raise ethical questions about what constitutes human life.
urrently scientists can carry out experiments on leftover embryos from IVF treatments, but they are in short supply and must be destroyed after 14 days. Scientists say that being able to create unlimited numbers of artificial embryos in the lab could speed up research while potentially removing some of the ethical boundaries.

 This is why RAM costs so much
This is why RAM costs so much

