
Breaking News
 Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
 COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
 Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
 Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Theoretical "supersolid" state of matter created in two separate studies
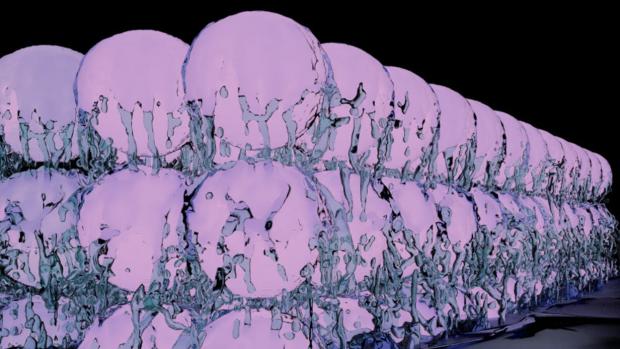
Now one such state, first proposed almost 50 years ago, has been created in experiments for the first time. Say hello to the supersolid, a state where atoms simultaneously exhibit a crystalline structure but still flow like a frictionless fluid.
The concept of a supersolid arose from the Nobel Prize-winning discovery in the 1970s of a superfluid, a liquid that has zero viscosity, meaning it flows with no resistance or "thickness." At the time, British physicist David Thouless theorized that a state of matter could exist where atoms are both free flowing like a superfluid, but also arranged in a crystalline structure, making it a supersolid.
Earlier attempts to produce this state used helium, the element that first exhibited superfluidity, but it was never brought to fruition. Now, two simultaneous – but independent – studies, one from ETH Zurich and one from MIT, have produced supersolids from Bose-Einstein condensates, using two different techniques.



