
Breaking News
 Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
 US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
 Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
 Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Top Tech News
 Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
 This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
 Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
CRISPR gene therapy is enhancing t-cell immnotherapy treatment of cancer and ...
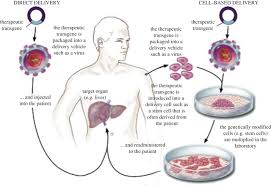
1. being more-effective tumor responses.
2. the targeted nature of CRISPR-mediated CAR integration into the genome might "prove safer than random integration, which carries the potential risk of generating a harmful mutation," Dr. Maus wrote.
3. It could enable off-the-shelf CAR T cells to be made that need not come from a patient's own T cells. This would enable easier and cheaper manufacture of CAR T cells.
New gene-editing technologies will likely lead to rapid improvement in antigen-targeted T-cell immunotherapies for cancer.
David Edgell, an associate professor of biochemistry at the University of Western Ontario, thinks CRISPR treatments could be available within the next two to three years, with modified T-cells used to treat some types of cancer (there are already clinical trials for lung cancer in China, and a similar one slated to take place at the University of Pennsylvania was approved last June by the National Institutes of Health

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

