
Breaking News
 300 WSM Ballistics Tables From Common Ammo Makers
300 WSM Ballistics Tables From Common Ammo Makers
 Oil Tankers Turning Off Transponders – 10% of Regular Volume in Dark Fleet Made Hormuz Passage
Oil Tankers Turning Off Transponders – 10% of Regular Volume in Dark Fleet Made Hormuz Passage
 Meet DARPA's X-76: The rotorcraft that flies like a jet
Meet DARPA's X-76: The rotorcraft that flies like a jet
 You've Been LIED to About Healthy Eating: The Truth Could Add Decades to Your Life
You've Been LIED to About Healthy Eating: The Truth Could Add Decades to Your Life
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
IBM has made Carbon nanotubes transistors smaller and faster than silicon
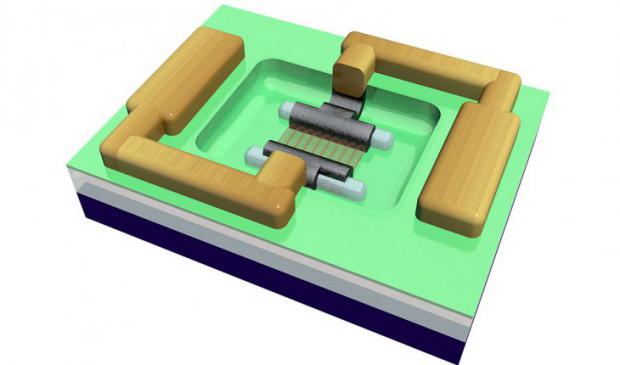
Now IBM and others will have to scale up superior carbon nanotube devices.
IBM scientists have been experimenting with carbon nanotubes, rolled-up sheets of carbon atoms just 1 nanometer, or a billionth of a meter, in diameter. But difficulties working with the material have meant that, for optimal performance, nanotube transistors have to be even larger than current silicon transistors, which are about 100 nanometers across. To cut that number down, a team of scientists used a new technique to build the contacts that draw current into and out of the carbon nanotube transistor. They constructed the contacts out of molybdenum, which can bond directly to the ends of the nanotubes, making them smaller. They also added cobalt so the bonding could take place at a lower temperature, allowing them to shrink the gap between the contacts. Another advance allowed for practical transistors.



