
Breaking News
 Catherine Fitts: Epstein, CIA Black Budget, the Control Grid, and the Banks' Role in War
Catherine Fitts: Epstein, CIA Black Budget, the Control Grid, and the Banks' Role in War
 "It's a disaster": Germans allowed to use oil and gas to heat their homes again
"It's a disaster": Germans allowed to use oil and gas to heat their homes again
 Victor Davis Hanson: Trump's Cost-Benefit Analysis For Striking Iran
Victor Davis Hanson: Trump's Cost-Benefit Analysis For Striking Iran
 Who is really running the world?
Who is really running the world?
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
MIT Envisions The First Space Hotel

How do you make research in space less expensive? Why not build a space station where half of the structure functions as a luxury hotel–and the other half belongs to NASA's astronauts?
That's the idea behind the Managed, Reconfigurable, In-space Nodal Assembly (or MARINA, for short), a conceptual design from five MIT graduate students that recently won the graduate division of NASA's Revolutionary Aerospace Systems Concepts design competition. Acting as a tenant of the space hotel concept would cost NASA about $360 annually–drastically less than what it costs to operate the International Space Station. It would save 16% of NASA's overall budget–about $3 billion per year.
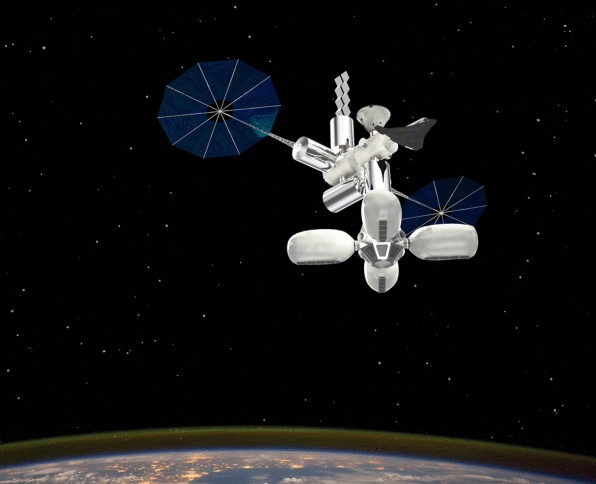
According to Matt Moraguez, a graduate student in MIT's Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics who led the proposal, MARINA has a modular design, with standardized interfaces that could connect any single point on the structure to any other. This standardization would allow other companies to create products and services for people living on MARINA–and create more possibilities for monetizing valuable space. Modularity would also enable the structure to transform into a vehicle for transporting people to Mars.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

