
Breaking News
 US Lawmakers Shmooze with Zelensky at Munich Security Conference...
US Lawmakers Shmooze with Zelensky at Munich Security Conference...
 Scientists have plan to save the world by chopping down boreal forest...
Scientists have plan to save the world by chopping down boreal forest...
 New Coalition Aims To Ban Vaccine Mandates Across US
New Coalition Aims To Ban Vaccine Mandates Across US
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Closer to Flash Memory Successor
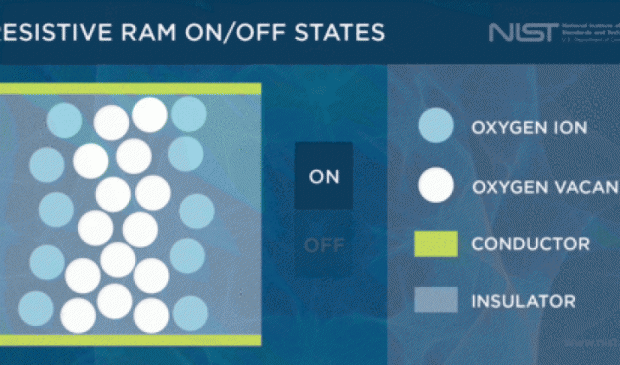
Nonvolatile memory is already familiar as the basis for flash memory in thumb drives, but flash technology has essentially reached its size and performance limits. For several years, the industry has been hunting for a replacement.
RRAM could surpass flash in many key respects: It is potentially faster and less energy-intensive. It also could pack far more memory into a given space—its switches are so small that a terabyte could be packed into a space the size of a postage stamp. But RRAM has yet to be broadly commercialized because of technical hurdles that need addressing.
RRAM switches are flipped on and off by an electrical pulse that moves oxygen ions around, creating or breaking a conductive path through an insulating oxide. NIST research shows that shorter, less energetic pulses are more effective at moving the ions the right amount to create distinct on/off states, potentially minimizing the longstanding problem of state overlap that has kept RRAM largely in the R&D stage. Credit: Hanacek and Nminibapiel/NIST
One hurdle is its variability. A practical memory switch needs two distinct states, representing either a one or a zero, and component designers need a predictable way to make the switch flip. Conventional memory switches flip reliably when they receive a pulse of electricity, but we're not there yet with RRAM switches, which are still flighty.

 Going the Way of the Denarius
Going the Way of the Denarius

