
Breaking News
 Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
 Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
 A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
 What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Breakthrough steel is far stronger, lower cost and process is applicable to Titanium
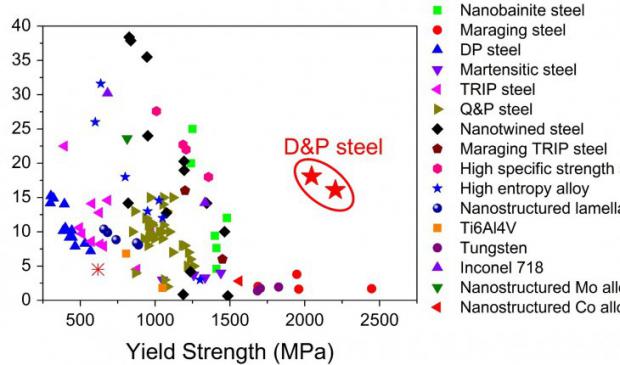
However, in some particular high-loading structural applications, metallic materials shall also have large ductility and high toughness to facilitate the precise forming of structural components and to avoid the catastrophic failure of components during service. Unfortunately, increasing strength often leads to the decrease in ductility, which is known as the strength-ductility trade-off. For example, ceramics and amorphous materials have negligible ductility, although they have great hardness and ultra-high strength. To simultaneously increase both strength and ductility of metallic materials using conventional industrial processing routes is both of great scientific and technological importance and is yet quite challenging in both the materials science community and industry sectors.



