
Breaking News
 Trump casually confirms first land strike on plant in Venezuela: 'We knocked that out'
Trump casually confirms first land strike on plant in Venezuela: 'We knocked that out'
 The End Game Has Begun For Our Current Financial System
The End Game Has Begun For Our Current Financial System
 Silver, Supply Chains, and the Reassertion of the Monroe Doctrine
Silver, Supply Chains, and the Reassertion of the Monroe Doctrine
 Ilhan Omar's Husband's Venture Capital Firm Removes Names From Website Under Scrutiny
Ilhan Omar's Husband's Venture Capital Firm Removes Names From Website Under Scrutiny
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Race for global low earth orbit high bandwidth internet satellites
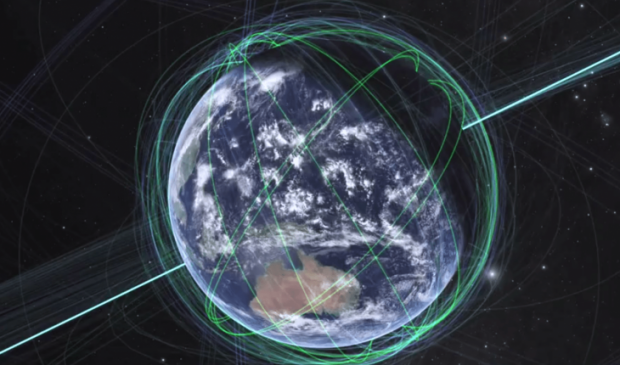
Low-earth orbit systems need complex software to run constellations of satellites and sophisticated antennas on the ground to aim at spacecraft zooming from horizon to horizon. Costs quickly overwhelm savings from building smaller gear.
Boeing is seeking approval for 60 satellites
OneWeb has FCC permission to serve the U.S. market using 720 satellites authorized by the U.K.
SpaceX's plan calls for 4,425 satellites, but it also has applied for an additional 7,518.
Two dozen ventures are raising money in an effort to fund global satellite networks.
Satellites in low-earth trajectories operate 200 to 1,200 miles above Earth and orbit it roughly every 90 minutes. Traditional communications satellites operate much higher, at an altitude of about 22,000 miles.
The LEO satellites will need to be massed produced cheaply and replaced every 4-5 years.



