
Breaking News
 Windows 11 QEMU/KVM Installation Guide in Linux Including TPM and Secure Boot
Windows 11 QEMU/KVM Installation Guide in Linux Including TPM and Secure Boot
 Silver: US Mint-Delays and Costco Limits Surface
Silver: US Mint-Delays and Costco Limits Surface
 Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
 O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The "Big Bang" of Alzheimer's: Breakthrough study uncovers genesis of the disease
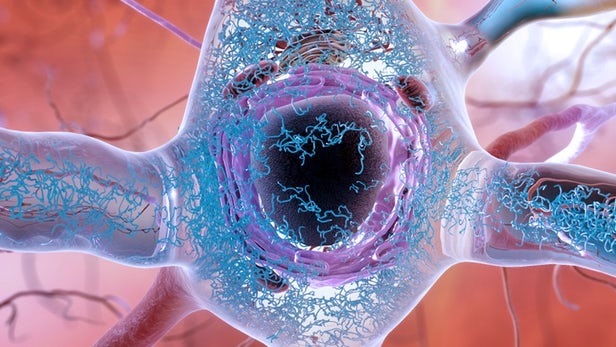
Impressive new research led by scientists at UT Southwestern, has discovered the earliest point in a neurodegenerative process that is thought to lead to dementia. The researchers describe the discovery as like finding the "Big Bang" of Alzheimer's disease, and it's hoped the work leads to new treatments and ways to detect the disease before major symptoms take hold.
"This is perhaps the biggest finding we have made to date," says Marc Diamond, a primary collaborator on this new study, "though it will likely be some time before any benefits materialize in the clinic. This changes much of how we think about the problem."
Much modern Alzheimer's research concentrates on a specific protein called amyloid beta, and the clumping of that protein is suspected as being the primary pathological cause of the disease's symptoms. But, after a long series of clinical trial failures in drugs designed to target those amyloid beta plaques, some scientists are turning their research attentions elsewhere.
This new research focuses on a different protein, called tau. These tau proteins have been found to form abnormal clumps in the brain, called neurofibrillary tangles, which can accumulate and kill neurons. Some researchers hypothesize that this is actually the primary causative source of Alzheimer's disease.
Until now it was not known how, or when, these tau proteins began to accumulate into tangles in the brain. It was previously believed that isolated tau proteins didn't have a distinctly harmful shape until they began to aggregate with other tau proteins. But the new research has revealed that a toxic tau protein actually presents itself as misfolded, exposing parts that are usually folded inside, before it begins to aggregate. It is these exposed parts of the protein that enable aggregation, forming the larger toxic tangles.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

