
Breaking News
 BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
 BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
 Aargh! Letters of marque would unleash Blackbeard on the cartels
Aargh! Letters of marque would unleash Blackbeard on the cartels
 How a Barter System Could Sustain Communities During a Supply Chain Collapse
How a Barter System Could Sustain Communities During a Supply Chain Collapse
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Electrons that behaves like light in twelve-sided graphene quasicrystal
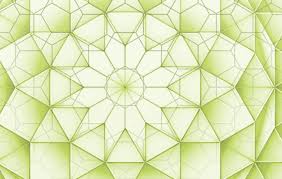
They have useful and unique electronic properties which are useful for probing new physics and they might be useful for spintronics and quantum computers. Those might be far faster forms of computing.
Electrons in monolayer graphene are described by massless Dirac electrons, which exhibit unique quantum phenomena due to the pseudospin and Berry phase of the massless electron.
A tunable bandgap up to 200 meV can be induced in bilayer graphene with electrical gating.
Dirac fermions in quasicrystalline graphene
Quasicrystal lattices, which can have rotational order but lack translational symmetry, can be used to explore electronic properties of materials between crystals and disordered solids. Ahn et al. grew graphene bilayers rotated exactly 30° that have 12-fold rotational order. Electron diffraction and microscopy confirmed the formation of quasicrystals, and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed anomalous interlayer electronic coupling that was quasi-periodic.



