
Breaking News
 Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
 Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
 The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
 Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Breakthrough Carbon nanotube bundles are over 20 times stronger than Kevlar
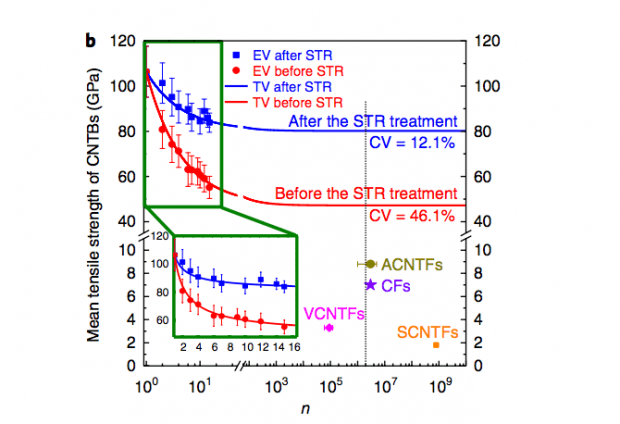
If a more rigorous engineering definition is used, the tensile strength of macroscale CNTBs is still 5–24 times that of any other types of engineering fiber, indicating the extraordinary advantages of ultralong Carbon nanotubes in fabricating superstrong fibers.
The work was done at Tsinghua University and other facilities in Beijing. Researchers were Yunxiang Bai, Rufan Zhang, Xuan Ye, Zhenxing Zhu, Huanhuan Xie, Boyuan Shen, Dali Cai, Bofei Liu, Chenxi Zhang, Zhao Jia, Shenli Zhang, Xide Li & Fei Wei.
A synchronous tightening and relaxing (STR) strategy further improves the alignment of the carbon nanotubes to increase the strength.
Superstrong fibers are in great demand in many high-end fields such as sports equipment, ballistic armour, aeronautics, astronautics and even space elevators. In 2005, the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched a 'Strong Tether Challenge', aiming to find a tether with a specific strength up to 7.5GPa cm3 per gram for the dream of making space elevators. Unfortunately, there is still no winner for this challenge. The specific strength of existing fibres such as steel wire ropes (about 0.05–0.33 GPa cm3 per gram), carbon fibres (about 0.5–3.5GPa cm3 per gram) and polymer fibers (about 0.28–4.14GPa cm3 per gram) is far lower than 7.5GPa cm3 per gram). Carbon nanotubes, with inherent tensile strength higher than 100GPa and Young's modulus over 1TPa, are considered one of the strongest known materials.



