
Breaking News
 NYU Prof: Trump's Whole Milk Push Is 'Dog Whistle To Far-Right'
NYU Prof: Trump's Whole Milk Push Is 'Dog Whistle To Far-Right'
 Local Police Are Finally Arresting Anti-ICE Agitators In Minnesota
Local Police Are Finally Arresting Anti-ICE Agitators In Minnesota
 Watch: Bondi Explodes Over Epstein During Shouting Match With Massie And Top Dems
Watch: Bondi Explodes Over Epstein During Shouting Match With Massie And Top Dems
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Thermal Energy Stored for Month in New Material
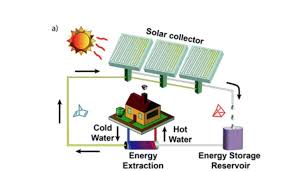
The amount of solar power in winter drops by 90%. Solar energy could provide a larger share of global power if there was a way to store all of the worlds energy usage for months. The development of solar energy can potentially meet the growing requirements for a global energy system beyond fossil fuels, but necessitates new scalable technologies for solar energy storage. Thermal energy can be used for a broad range of applications such as domestic heating, industrial process heating and in thermal power processes. One promising way to store solar thermal energy is so-called molecular solar thermal (MOST) energy storage systems, where a photoswitchable molecule absorbs sunlight and undergoes a chemical isomerization to a metastable high energy species. Here we present an optimized MOST system (providing a high energy density of up to 0.4 MJ kg−1), which can store solar energy for a month at room temperature and release the thermochemical energy "on demand" in a closed energy storage cycle. In addition to a full photophysical characterization, solar energy capture of the present system is experimentally demonstrated by flowing the MOST system through an outdoor solar collector (≈900 cm2 irradiated area). Moreover, catalyst systems were identified and integrated into an energy extraction device leading to high temperature gradients of up to 63 °C (83 °C measured temperature) with a short temperature ramp time of only a few minutes. The underlying step-by-step mechanism of the catalytic reaction is modelled in detail using quantum chemistry calculations, successfully rationalizing the experimental observations.

 A Defense of 1950s Housewives
A Defense of 1950s Housewives


