
Breaking News
 Rand Paul just revealed he's working with RFK Jr. to prosecute Fauci. But Trump's DOJ is ign
Rand Paul just revealed he's working with RFK Jr. to prosecute Fauci. But Trump's DOJ is ign
 BREAKING EXCLUSIVE: "I Think Bill Gates Is The Boss," Epstein Survivor Claims Gates Was...
BREAKING EXCLUSIVE: "I Think Bill Gates Is The Boss," Epstein Survivor Claims Gates Was...
 Musk Offers Free Starlink As Iran Protests Endure Internet, Comms Blackout
Musk Offers Free Starlink As Iran Protests Endure Internet, Comms Blackout
 South Korea Seeks Death Penalty For Ex-President Yoon's Botched Martial Law Attempt
South Korea Seeks Death Penalty For Ex-President Yoon's Botched Martial Law Attempt
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
Routine Eye Test Can Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer's in Seconds...
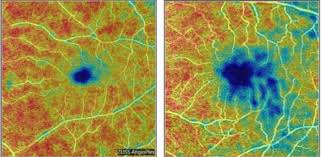
A routine eye test can detect the earliest stages of Alzheimer's disease in seconds, according to new research.
The non-invasive scan looks for changes in blood vessels in the retina. Tiny alterations in this small piece of tissue mirror those going on in the brain and are the first signs of dementia, say scientists.
The technique, which is called OCTA (optical coherence tomography angiography), could revolutionize treatment of the devastating neurological disorder because it enables early diagnosis. Physicians can now see blood vessels in the back of the eye that are smaller than the width of a human hair.
Senior author Professor Sharon Fekrat, an ophthalmologist at the Duke Eye Center in Durham, North Carolina, said: "If we can detect these blood vessel changes in the retina before any changes in cognition, that would be a game-changer."

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

