
Breaking News
 Which party represents Americans?
Which party represents Americans?
 Even The Best AI Scenario Is The End Of Everything We've Ever Been
Even The Best AI Scenario Is The End Of Everything We've Ever Been
 In Simulated War Games, Top AI Models Recommended Using Nukes 95% Of The Time
In Simulated War Games, Top AI Models Recommended Using Nukes 95% Of The Time
 Rising Cancer Rates, the Globalist Agenda, and the Big Business Land Grab Making You Poor
Rising Cancer Rates, the Globalist Agenda, and the Big Business Land Grab Making You Poor
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Gene therapy for color blindness passes first phase of human testing
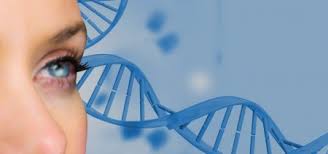
Total color blindness, or achromatopsia, is generally an inherited disease caused by mutations in one of six different genes, with the majority of cases involving variants in either the CNGA3 or CNGB3 genes. The new gene therapy being trialed focuses on correcting a defect in the CNGA3 gene.
The treatment is somewhat similar to one of the first FDA-approved gene therapies, for vision loss, called Luxturna. These treatments attach a healthy functioning gene to a genetically modified harmless virus. The treatment is injected into a patient's eye and hopefully the correctly functioning gene begins producing whatever protein was previously missing, helping cure the condition caused by the defective gene.



