
Breaking News
 Democrats Announce State Of The Union Response Will Be Delivered By Bad Bunny
Democrats Announce State Of The Union Response Will Be Delivered By Bad Bunny
 American Attack on Iran: World War
American Attack on Iran: World War
 If You Think the US Wants To Bring Democracy to Iran, Watch What They're Currently Doing to Iraq
If You Think the US Wants To Bring Democracy to Iran, Watch What They're Currently Doing to Iraq
 The Scary Truth About Living in Big Cities During the Turbulent Times Ahead
The Scary Truth About Living in Big Cities During the Turbulent Times Ahead
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Soft-bodied robot channels the cheetah to move fast
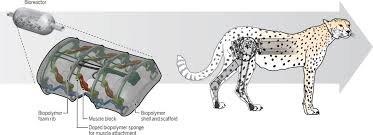
The world's fastest land animal, cheetahs run by rapidly flexing their spines between two stable states. A consortium of American scientists recently set out to replicate that motion in a soft robot. The resulting device is known as LEAP, which stands for "Leveraging Elastic instabilities for Amplified Performance."
Instead of muscles and a biological spine, the silicone-bodied robot incorporates two soft pneumatic actuators and a flexible spring-loaded mechanical spine. Alternately pumping air in and out of the two actuators causes energy to be stored and suddenly released, triggering the spring to instantly flex the spine from one stable state to another. As a result, the bot is able to exert force against the ground, leaping off of it.
Utilizing this technique, LEAP is able to gallop at a rate of up to 2.7 body lengths per second across flat, solid surfaces.



