
Breaking News
 The First Automated Rammed Earth House Building Machine - Form Earth
The First Automated Rammed Earth House Building Machine - Form Earth
 We Build and Test Microwave Blocking Panels - Invisible to Radar
We Build and Test Microwave Blocking Panels - Invisible to Radar
 California Rebuild: Crushing Rules, Empty Reservoirs, Angry Residents
California Rebuild: Crushing Rules, Empty Reservoirs, Angry Residents
 Episode 493 - War in Iran! (Bored of Peace Edition)
Episode 493 - War in Iran! (Bored of Peace Edition)
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Gryphon Technologies to develop nuclear rocket engine for DARPA
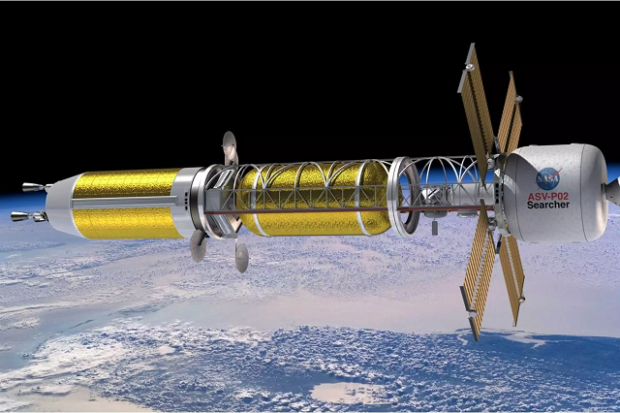
DARPA has awarded a US$14-million contract to the Gryphon Technologies engineering firm to develop and demonstrate a nuclear rocket engine for the agency's Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO) program. The High-Assay Low Enriched Uranium (HALEU) Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) system will allow the US military to carry out missions in cislunar space.
The single greatest limitation in space travel is the propulsion system. On Earth, it's possible to create motors that have a very high payload ratio, so one can, in the words of an early aviator, make a tea tray fly by putting enough power behind it. However, getting into space requires such high velocities and such high energies that engineers are forced to use very large engines and huge amounts of fuel to put very small payloads into orbit.
Once in space, there are essentially two options. One is to use chemical rockets, but these have largely reached their theoretical limits when it comes to thrust, or eclectic propulsion systems that produce very small thrust for very long periods of time.
As far back as 1945, it was recognized that there was a third option, which is to harness the power of the atom to produce a rocket that is more powerful than its chemical counterparts. The problem has been to create a practical design that produces enough thrust to warrant the investment.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

