
Breaking News
 Is the White House Actually the Overlook Hotel East?
Is the White House Actually the Overlook Hotel East?
 QatarEnergy Declares Force Majeure As One-Fifth Of Global LNG Supply Goes Dark
QatarEnergy Declares Force Majeure As One-Fifth Of Global LNG Supply Goes Dark
 Primary Losers: Crockett Cries 'Disenfranchisement', Crenshaw Crushed
Primary Losers: Crockett Cries 'Disenfranchisement', Crenshaw Crushed
 U.S. Submarine Sinks Iranian Warship In First Torpedo Kill Since WWII
U.S. Submarine Sinks Iranian Warship In First Torpedo Kill Since WWII
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Microwave Water Splitting for Breakthroughs for Making Hydrogen, Oxygen and Fast Battery
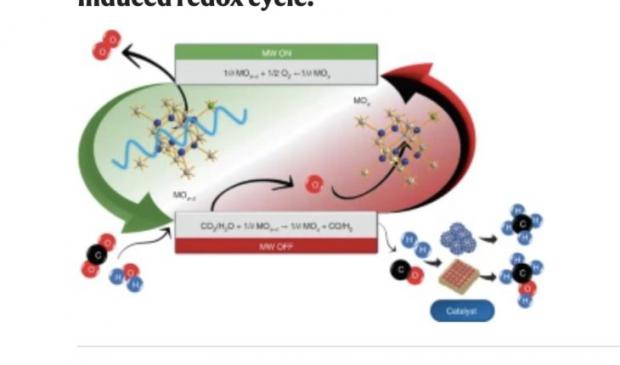
Researchers from the Polytechnic University of Valencia and the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) report contactless H2 production via water electrolysis mediated by the microwave-triggered redox activation of solid-state ionic materials at low temperatures (less than 250 °C).
This will simplify and significantly cheapen the process for hydrogen production.
Water was reduced via reaction with non-equilibrium gadolinium-doped CeO2 that was previously in situ electrochemically deoxygenated by the sole application of microwaves. The microwave-driven reduction was identified by an instantaneous electrical conductivity rise and O2 release. This process was cyclable, whereas H2 yield and energy efficiency were material- and power-dependent. Deoxygenation of low-energy molecules (H2O or CO2) led to the formation of energy carriers and enabled CH4 production when integrated with a Sabatier reactor. This method could be extended to other reactions such as intensified hydrocarbons synthesis or oxidation.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

