
Breaking News
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: February 22, 2026 Edition
 The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Scientists Have Created Programmable Robots Made of LIVING TISSUE. What Could Possibly Go Wrong?

Everyone knows that robots aren't living beings right? Well, we did. That is, until scientists and developers recently announced how they have bridged some of that gap between living and non-living beings.
This new development is a combination of artificial intelligence and biology. In fact, only this week, a research of roboticists and scientists published what is being referred to as a "recipe for making a new lifeform" called xenobots. The xenobots are made from stem cells and the term xeno comes from the frog cells (xenopus laevis) which are used to make them.
One of the researchers involved described the new creation as "neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal" but instead it is a "new class of artifact: a living, programmable organism."
File this under "What Could Possibly Go Wrong?"
What is a xenobot?
The xenobots are less than 1mm long and are contain 500-1000 living cells. They have a number of shapes, mostly simplistic with some having squat "legs." They are able to propel themselves in linear or circular directions, move small objects, and join together to act collectively. They are able to live up to ten days using their own cellular energy.
Scientists claim that these new "reconfigurable biomachines" can improve human and animal health, but there are many concerns from legal and ethical standpoints.

 TGIF: Immigration and Culture
TGIF: Immigration and Culture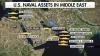 Does It Smell Like Victory?
Does It Smell Like Victory?


