
Breaking News
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: February 22, 2026 Edition
 The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Surpassing Optical Limit for 28000 Times Blu-Ray Storage on a 12 Centimeter Disk
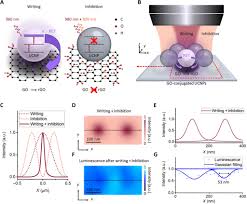
A separate advance with in data encoding could triple storage to 2.1 Petabytes in a single optical disk.
Researchers at USST, RMIT and NUS have overcome the optical diffraction limit by using earth-rich lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide flakes. This unique material platform enables low-power optical writing nanoscale information bits.
The higher density system will use inexpensive continuous-wave lasers. This will have lower operating costs compared to traditional optical writing techniques using expensive and bulky pulsed lasers.
Next generation of high-capacity optical data storage technology will also enable the development of energy-efficient nanofabrication of flexible graphene based electronics.

 TGIF: Immigration and Culture
TGIF: Immigration and Culture Does It Smell Like Victory?
Does It Smell Like Victory?


