
Breaking News
 The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
The Domino Effect: How a U.S. Attack on Iran Could Unleash Global Catastrophe
 The True History of Glyphosate, Derived from Deadly Organophosphate Nerve Agents like Sarin...
The True History of Glyphosate, Derived from Deadly Organophosphate Nerve Agents like Sarin...
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
How an extra thumb changes the way your brain perceives the hand
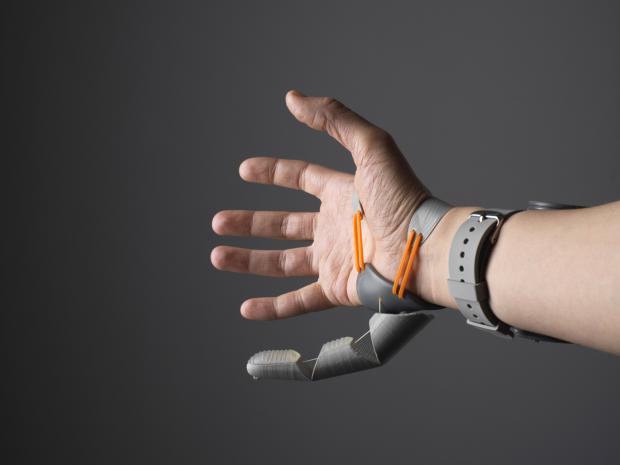

The project was more a novelty than a prototype, exploring futurist ideas surrounding body augmentation.
A team of neuroscientists working in The Plasticity Lab at University College London saw the Third Thumb on the news and immediately contacted Clode. They were studying how the human brain adapts to operate augmentative technology, and the Third Thumb was a perfect device to incorporate into their research.
"Body augmentation is a growing field aimed at extending our physical abilities, yet we lack a clear understanding of how our brains can adapt to it," explains Tamir Makin, head of the Plasticity Lab and lead author on the new research. "By studying people using Dani's cleverly-designed Third Thumb, we sought to answer key questions around whether the human brain can support an extra body part, and how the technology might impact our brain."
The researchers recruited 20 subjects who each spent five days training in the lab to use the Third Thumb. They were encouraged to take the device home with them each evening and try to use it for between two and six hours in total per day.
At the beginning and end of the study all participants were scanned using MRI to track brain activity while moving their fingers. A control group of ten participants were also recruited. They completed the same five day training protocol but used a static version of the Third Thumb.

 TGIF: Immigration and Culture
TGIF: Immigration and Culture Does It Smell Like Victory?
Does It Smell Like Victory?


