
Breaking News
 Free Ian Freeman: Defend Financial Privacy and Justice - Sign the petition
Free Ian Freeman: Defend Financial Privacy and Justice - Sign the petition
 Charlie Robinson with Tim James, Marjory Wildcraft & Patrick Henningsen:
Charlie Robinson with Tim James, Marjory Wildcraft & Patrick Henningsen:
 It's Time To Reopen The Franklin Child Prostitution Case After Epstein Revelations
It's Time To Reopen The Franklin Child Prostitution Case After Epstein Revelations
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Fermented vs. high-fiber diet microbiome study delivers surprising results
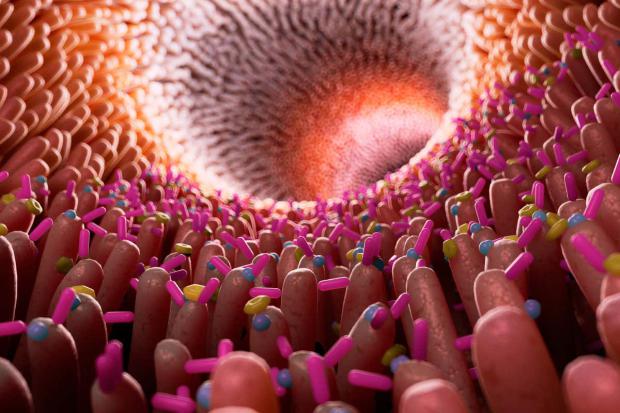
Investigating the relationship between diet, gut bacteria and systemic inflammation, a team of Stanford University researchers has found just a few weeks of following a diet rich in fermented foods can lead to improvements in microbiome diversity and reductions in inflammatory biomarkers.
The new research pitted a high-fiber diet against a diet with lots of fermented food. Thirty-six healthy adults were recruited and randomly assigned one of the two diets for 10 weeks.
"We wanted to conduct a proof-of-concept study that could test whether microbiota-targeted food could be an avenue for combatting the overwhelming rise in chronic inflammatory diseases," explains Christopher Gardner, co-senior author on the new study.
Blood and stool samples were collected before, during, and after the dietary intervention. Over the course of the trial the researchers saw levels of 19 inflammatory proteins drop in the fermented food cohort. This was alongside increases in microbial diversity in the gut and reduced activity in four types of immune cells.
Perhaps most significantly, these changes were not detected in the group tasked with eating a high-fiber diet. Erica Sonnenburg, another co-senior author on the study, says this discordancy between the two cohorts was unexpected.
"We expected high fiber to have a more universally beneficial effect and increase microbiota diversity," she says. "The data suggest that increased fiber intake alone over a short time period is insufficient to increase microbiota diversity."

 The Question Not Being Asked
The Question Not Being Asked

