
Breaking News
 Doug Casey on Donahue 3 Nov 1980 - Just as Relevant TODAY as it was 38 Years ago
Doug Casey on Donahue 3 Nov 1980 - Just as Relevant TODAY as it was 38 Years ago
 Yes, silver is going parabolic but it is important to put things in perspective...
Yes, silver is going parabolic but it is important to put things in perspective...
 As gold approaches $5,100, to the chagrin of CNBC, I recall the days when they still had me...
As gold approaches $5,100, to the chagrin of CNBC, I recall the days when they still had me...
 Don't Tread on the First Amendment:
Don't Tread on the First Amendment:
Top Tech News
 Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
World's tiniest camera -- the size of a grain of salt -- created by scientists
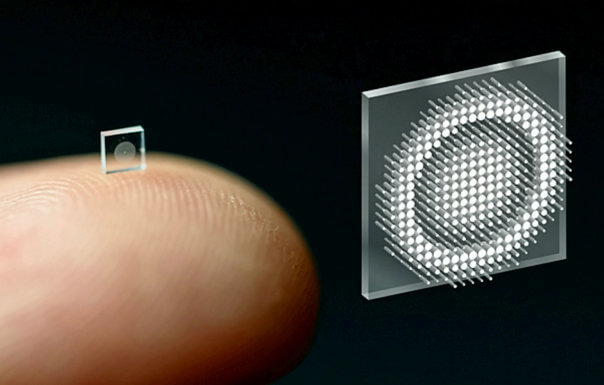
Computer scientists from Princeton University and the University of Washington say the small device they created can take crisp, full-color pictures just as well as conventional cameras which are 500,000 times bigger.
The new technology may help doctors to diagnose and treat diseases far less invasively than traditional endoscopy can today. It will also make imaging better, as thousands of tiny devices could cover the whole surface of a smartphone to become one giant camera — instead of mobile devices needing three different cameras to take pictures.
Traditional cameras use several curved glass or plastic lenses to bend light rays into focus, but the new device uses a "metasurface" which developers can make just like a computer chip. The metasurface is just half a millimeter wide and is made up of 1.6 million tiny posts, which are all shaped like cylinders but none of them look exactly the same.
When the antennae-like tiny posts interact with light, with the help of algorithms, they produce better pictures and capture a wider frame of view than any full-color metasurface camera created so far. The metasurfaces are made from silicon nitride, a glass-like material which can be manufactured easily and produced more cheaply than lenses in conventional cameras.
Older metasurfaces took poor pictures
Senior study author Dr. Felix Heide notes that a key innovation during the camera's development was figuring out how to combine the design of the optical surface with the signal processing algorithms that make an image.
The team adds that this integrated design boosted the camera's performance in natural light. Previous metasurface cameras have required the pure laser light of a laboratory or other ideal conditions in order to create high-quality images.



