
Breaking News
 U.S. evacuates 20,000 citizens as Middle East war intensifies
U.S. evacuates 20,000 citizens as Middle East war intensifies
 MAJOR GLOBAL ECONOMIC CRISIS UPDATE: The Closure Of The Strait of Hormuz For Just 4 Days...
MAJOR GLOBAL ECONOMIC CRISIS UPDATE: The Closure Of The Strait of Hormuz For Just 4 Days...
 Counting The Costs: Another War Is Not What America Needed
Counting The Costs: Another War Is Not What America Needed
 Researchers Train Bacteria to Consume Tumors from the Inside Out
Researchers Train Bacteria to Consume Tumors from the Inside Out
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Adding new letters to DNA alphabet doubles density of data storage
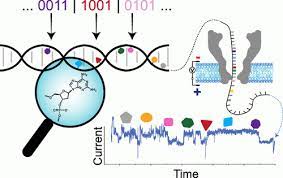
DNA is naturally made up of combinations of four nucleobases: adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. Represented by the letters A, G, C and T, these bases group together in different sequences to form blueprints for every living organism. And this information storage system is incredibly dense, with a single gram of DNA capable of storing up to 215 petabytes (215 million GB) of data.That of course makes it a very attractive potential storage solution for the huge amounts of data modern society produces daily – the entire contents of the internet could fit in a shoebox full of DNA. And as if that storage wasn't dense enough, the researchers on the new study have found a way to double it.



