
Breaking News
 Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
 Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
 The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
 Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
New shock-absorbing material as strong as metal but light as foam
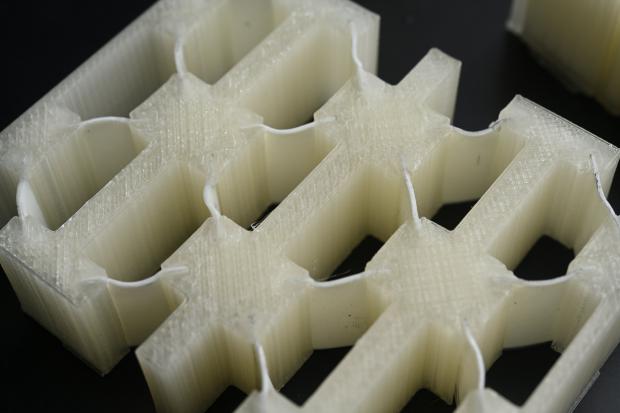
The stuff could make for helmets, armor and vehicle parts that are lighter, stronger and, importantly, reusable.
The key to the new material is what are known as liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs). These are networks of elastic polymers in a liquid crystalline phase that give them a useful combination of elasticity and stability. LCEs are normally used to make actuators and artificial muscles for robotics, but for the new study the researchers investigated the material's ability to absorb energy.
The team created materials that consisted of tilted beams of LCE, sandwiched between stiff supporting structures. This basic unit was repeated over the material in multiple layers, so that they would buckle at different rates on impact, dissipating the energy effectively.
In a series of experiments, the team tested how well the material could withstand impacts of different masses at different speeds. The materials were struck by objects weighing between 4 and 15 lb (1.8 and 6.8 kg) at speeds of up to 22 mph (35.4 km/h) and, sure enough, they held up.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the material performed better with more layers of the cells. A structure with four layers, for example, had almost double the energy absorption density of a single-layer structure.
While the materials were so far only tested with impacts up to 22 mph, the team says that they should be able to absorb impacts at higher speeds as well.
The researchers say that the material could be used to improve the safety of helmets, body armor, car bumpers and other parts of vehicles and aircraft, effectively dissipating energy from impacts while remaining lightweight.



