
Breaking News
 America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
America's Streets Are Filled With Poop, And Billions Of Gallons Of Untreated Wastewater...
 3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
3 Million Pages of Child Sex Trafficking, So, What Is the FBI Doing?
 Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
Communists Once Again Suck At Hockey
 Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Grand Theft World Podcast 274 | Epstein Apocalypse with Guest Santos Bonacci
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Lasers and ultrasound combine to pulverize arterial plaque
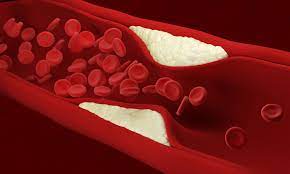
By bringing ultrasound into the mix, scientists at the University of Kansas have demonstrated a new take on this treatment that relies on exploding microbubbles to destroy plaque with greater safety and efficiency, while hinting at some unique long-term advantages.
The novel ultrasound-assisted laser technique builds off what's known as laser angioplasty, an existing treatment designed to improve blood flow in patients suffering from plaque buildup that narrows the arteries. Where more conventional treatments such as stents and balloon angioplasty expand the artery and compress the plaque, laser angioplasty destroys it to eliminate the blockage.
The laser is inserted into the artery with a catheter, and the thermal energy it generates turns water in the artery into a vapor bubble that expands, collapses and breaks up the plaque. Because this technique calls for high-power lasers, it has the potential to perforate or dissect the artery, something the scientists are looking to avoid by using low-power lasers instead.
They were able to do so in pork belly samples and ex vivo samples of artery plaque with the help of ultrasound. The method uses a low-power nanosecond pulsed laser to generate microbubbles, and applying ultrasound to the artery then causes these microbubbles to expand, collapse and disrupt the plaque.



