
Breaking News
 Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
Marjorie Taylor Greene EVISCERATES Trump Over Iran War! w/ Rick Overton
 Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
Sip your way to better gut health with these science-backed, fermented beverages
 The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
The War on Sunlight Is Real (And It's Not an Accident) | Dr. Jack Kruse
 Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Trump's Unconditional Surrender, NEW Supreme Leader Mojtaba Khamenei + NYC IED Attack...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Piezoelectric "bone bandage" heals cracked bones faster
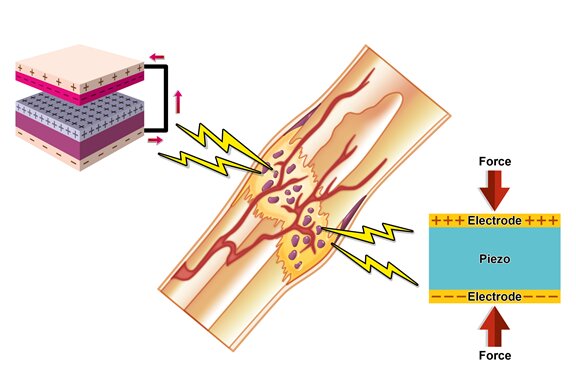
The novel "bone bandage" has wide-ranging potential applications for bone regeneration and regenerative medicine generally.
Piezoelectric materials generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress. Bone is a piezoelectric material. Because it possesses an electrical microenvironment, electrical signals play an important role in the bone repair process, which can effectively promote bone regeneration. However, bone regeneration is a complex process that relies on mechanical, electrical, and biological components.
Current strategies for bone regeneration, such as grafts or scaffolds that release growth factors, have limitations, such as complications at the donor site, limited availability, and high cost. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a pioneering approach to bone regeneration that combines piezoelectricity and a mineral that occurs naturally in bone.
Hydroxyapatite (HAp), a mineral in bones and teeth, plays a role in bone's structural strength and regeneration. It's commonly added to toothpaste to remineralize tooth enamel and fortify teeth. Studies have found that HAp enhances osteogenesis (bone formation) and provides a scaffold for new bone growth. It also has piezoelectric properties and a rough surface, making it an ideal candidate for creating scaffolds on which to grow bone.
So, the researchers fabricated a freestanding biomimetic scaffold, integrating HAp within the piezoelectric framework of polyvinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoro ethylene (P(VDF-TrFE)), a polymer film. The independent scaffold, which generates electrical signals when pressure is applied, sets this approach apart from previous research combining HAp and P(VDF-TrFE), which was limited to coatings on metallic prosthetics. The researchers' novel approach, they say, provides a versatile platform for bone regeneration beyond surface-bound applications.



