Breaking News
 Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
Jake Paul - Trump interview: We cover the Iran war, immigration policies, the assassination...
 US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
US Attorney Jeanine Pirro just announced activist Judge Boasberg has BLOCKED a Grand Jury...
 Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
Cost of the Iran War--and Why It Will Fuel Inflation
 Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Senator Ted Cruz Says "Christ Is King" Means "I Hate The Jews" & Jews, Not Chris
Top Tech News
 Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
Musk Whips Out 'Macrohard' In Disruptive Tesla-xAI Bid To Shaft Software Companies
 This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
This Bonkers Folding X-Plane Is One Step Closer to Hitting the Skies
 Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
Smart 2-in-1 digital microscope goes desktop or handheld as needed
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
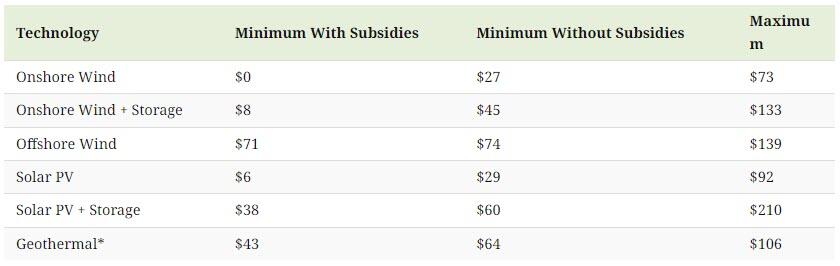
These Are America's Cheapest Sources Of Electricity In 2024
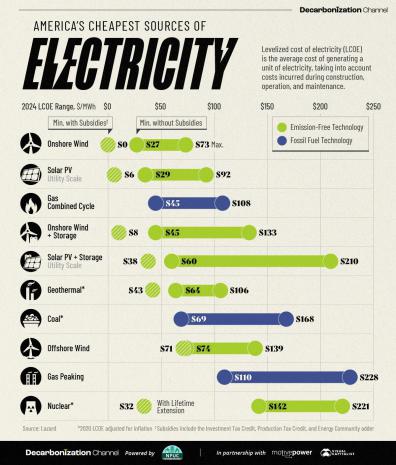
This chart, created by Visual Capitalist's Selin Oguz and Ryan Bellafontaine, in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, shows which electricity sources are the most and least expensive in 2024, using data by Lazard.
Onshore Wind and Solar: A Bargain with Subsidies
Onshore wind power effectively costs $0 per megawatt-hour (MWh) when subsidies included in the Inflation Reduction Act, such as the Investment Tax Credit, Production Tax Credit, and Energy Community Adder, are applied.
Demand for storage solutions is rising quickly. If storage is included, the minimum cost for onshore wind increases to $8 per MWh. Offshore wind, while more expensive, still presents a competitive option at a minimum of $71 per MWh with subsidies.
*2020 LCOE adjusted for inflation
Solar photovoltaics (PV) have similarly attractive economics.
With subsidies, the minimum cost is $6 per MWh. When including storage, $38 per MWh. Notably, the maximum cost of solar PV with storage has significantly increased from $102 in 2023 to $210 in 2024, although the cost of solar alone is still 83% cheaper in 2024 than it was in 2009, according to Lazard.
The inflation of 2022–2023 took a toll on solar PV and onshore wind, pushing their maximum unsubsidized costs back up to where they were in 2013 and 2015, respectively. However, solar PV dropped by $4 and onshore wind by $2 from 2023–2024.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.