
Breaking News
 Wash Post Editorial Board Turns Against Climate Agenda?!
Wash Post Editorial Board Turns Against Climate Agenda?!
 One Year Ago I Predicted and Described in Detail Huge Mars AI Plans that Elon Musk Confirmed...
One Year Ago I Predicted and Described in Detail Huge Mars AI Plans that Elon Musk Confirmed...
 British Teachers To "Spot Misogyny" In Boys And Target Them For Reeducation
British Teachers To "Spot Misogyny" In Boys And Target Them For Reeducation
 Democrats Refuse To Release Post-Mortem Of 2024 Election Loss, DNC Chair Says
Democrats Refuse To Release Post-Mortem Of 2024 Election Loss, DNC Chair Says
Top Tech News
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
 Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
 PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
 Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
 'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
A Furry Diving Suit Could Keep You Warm
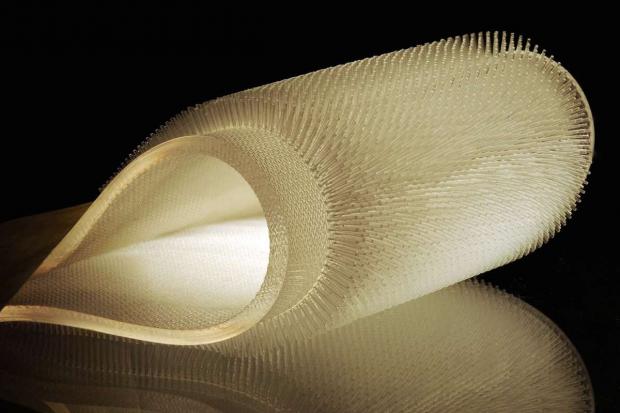
Whereas dolphins and whales rely on thick blubber to help keep warm in cold water, fur seals and sea otters depend on dense fur to trap a layer of air against their bodies. Since air does not conduct heat as well as water, air layers can insulate against heat loss.
Now mechanical engineer Alice Nasto at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created artificial mimics of such fur to see how these hairs protect these seafaring creatures.
"Our research group studies a lot of biologically inspired fluid mechanics problems, such as how snails use slime for locomotion, or how water striders walk on water," Nasto says.
The researchers used laser-cut acrylic molds to fabricate hairy surfaces made of silicone rubber. They next experimented with the effects that hair properties such as hair length and hair spacing had when these materials were plunged at precise speeds into liquids such as silicone oil, which comes in a variety of viscosities.



