
Breaking News
DRINK 1 CUP Before Bed for a Smaller Waist
 Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
 Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
 WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Researchers Have Preserved An Entire Rabbit Brain
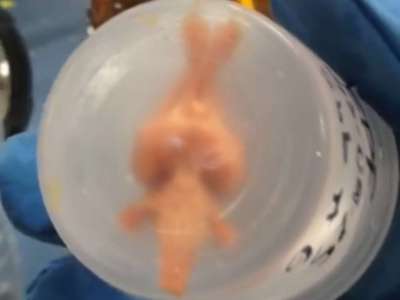
Five years ago, a non-profit organization called the Brain Preservation Foundation (BPF) challenged the world's neuroscience community to a tough task: to preserve a mouse brain (or a mammalian brain of equal size) for extreme long-term storage. All the neurons and synapses within it would have to remain intact and visible while viewed under a special electron microscope. If achieved, the accomplishment would allow scientists not only to have a better way of studying and possibly treating brain diseases, but it would also pave the way to the idea that we might someday be able to preserve the memory stored in the brain's trillions of microscopic connections.

Kenneth Hayworth/The Brain Preservation Foundation
Robert McIntyre taking a rabbit brain out of a -135 degrees Celsius freezer unit after overnight storage. The brain is completely solid.
Five years ago, a non-profit organization called the Brain Preservation Foundation (BPF) challenged the world's neuroscience community to a tough task: to preserve a mouse brain (or a mammalian brain of equal size) for extreme long-term storage. All the neurons and synapses within it would have to remain intact and visible while viewed under a special electron microscope. If achieved, the accomplishment would allow scientists not only to have a better way of studying and possibly treating brain diseases, but it would also pave the way to the idea that we might someday be able to preserve the memory stored in the brain's trillions of microscopic connections.
Today, BPR has announced that a project done by 21st Century Medicine and led by Robert McIntyre, a recent graduate of MIT, has won the prize and brought the five-year race to a successful end. The team was awarded $26,735 for their work.



