
Breaking News
 Trudeau's Emergency Powers Ruled ILLEGAL
Trudeau's Emergency Powers Ruled ILLEGAL
 Antifa Protests Violence By Viciously Beating Bystanders
Antifa Protests Violence By Viciously Beating Bystanders
Top Tech News
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
Scientists successfully 3D print a functioning human ear
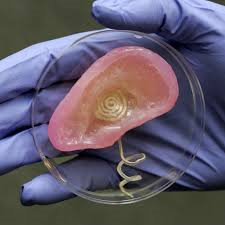
This remarkable achievement was made possible by the recently debuted Integrated Tissue and Organ Printing System (ITOP) designed by a research team led by Anthony Atala from Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine to replace damaged or missing body parts. The team further demonstrated ITOP's capabilities by 3D printing a jaw bone, muscle tissue, and cartilage structures.
The ITOP system creates its artificial human body parts in a manner similar to other 3D printers, which apply layer upon layer to build a product in a process called additive manufacturing. Rather than plastic or metal, ITOP uses specially designed biomaterials that closely emulate the structure of actual living tissue. Prior to ITOP, existing printers were challenged by the need to create tissues of sufficient strength.

 Monsters of the Deep
Monsters of the Deep Dark Kiev
Dark Kiev


