
Breaking News
 IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: December 28, 2025 Edition
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Spongy Implants Can Replace Cancerous Vertebrae
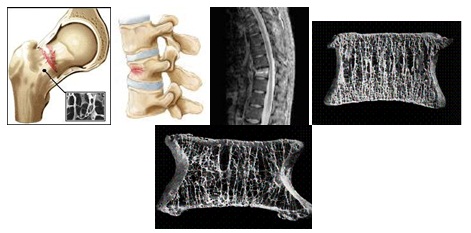
Cancer becomes significantly more deadly when it spreads throughout the body. Some types of cancers, like breast and prostate, are more likely to spread to the bones, and the spine is the most common site for those metastases. If doctors have to surgically remove a vertebrae, they can replace it with metal cages or bone grafts, which require an invasive surgery to implant, or they can implant titanium rods, which are less invasive to put in but are expensive.
Now researchers from the Mayo Clinic have created a spongy, expandable material that can take the place of cancerous vertebrae that have been surgically removed. They are presenting their work this week at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
The researchers were looking to create a material that surgeons would be able to implant relatively non-invasively, so it would need to be compact, but also flexible enough to completely fill the empty space left by the missing vertebrae. And, ideally, it would be less expensive than the titanium rods, which can cost many thousands of dollars for just one patient.



