
Breaking News
 Tucker Exposes Trump Would-Be Assassin Thomas Crooks' Social Media History, The FBI Coverup...
Tucker Exposes Trump Would-Be Assassin Thomas Crooks' Social Media History, The FBI Coverup...
 This Was A Major Red Flag In 2008, And Now It Is Happening Again!
This Was A Major Red Flag In 2008, And Now It Is Happening Again!
 Trump orders DOJ probe into Epstein's alleged ties with JPMorgan, Clinton and other Democrats
Trump orders DOJ probe into Epstein's alleged ties with JPMorgan, Clinton and other Democrats
Top Tech News
 Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
 China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
 Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
 Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
 SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
 Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
 HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
 What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
Gene Therapy For Congenital Blindness Has Long-Lasting Effect
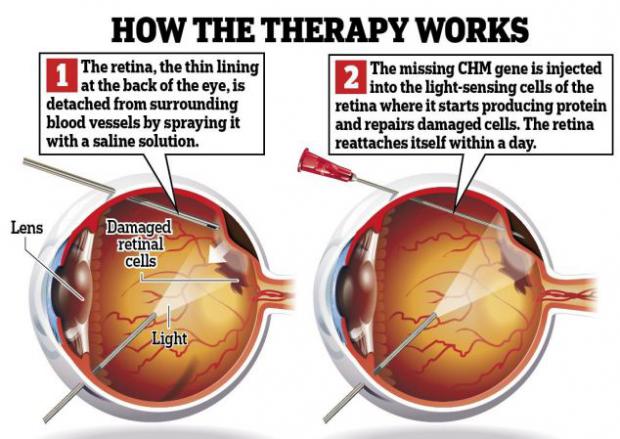
For the one in 50,000 people born with the genetic disorder choroideremia, there's no treatment that can slow the progressive vision loss. Scientists from the University of Oxford have been developing a gene therapy treatment to reverse the effects of the disease, and, though the initial results seemed promising, they had not been sure the treatment would work in the long term.
According to a study published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, the treatment has worked well in patients over the course of four years, buoying hopes that treatment for the condition (and for other genetic degenerative eye conditions like retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration) may become available to other patients soon.
Many gene therapy treatments have been focused on conditions that affect the eyes. These diseases are often caused by just one or two genes, the eyes are easy to access to administer the treatment, and results are often easy to detect by comparing a patient's treated and untreated eyes.

 A WORLD OF DEBT
A WORLD OF DEBT
 Unbanked In A Connected World
Unbanked In A Connected World

