
Breaking News
 Japanese biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi won the Nobel Prize for discovering how the body...
Japanese biologist Yoshinori Ohsumi won the Nobel Prize for discovering how the body...
 IT BYPASSES THE RETINA. IT BYPASSES THE OPTIC NERVE. IT SENDS IMAGES STRAIGHT...
IT BYPASSES THE RETINA. IT BYPASSES THE OPTIC NERVE. IT SENDS IMAGES STRAIGHT...
 PROMOTING THE NATIONAL DEFENSE BY ENSURING AN ADEQUATE SUPPLY OF...
PROMOTING THE NATIONAL DEFENSE BY ENSURING AN ADEQUATE SUPPLY OF...
 REAL-ID, Mail-Order CDLs, and America's CDL Free-for-All.
REAL-ID, Mail-Order CDLs, and America's CDL Free-for-All.
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Wisdom Teeth Contain Unique Stem Cell That Can Form Cartilage, Neurons, and Heart Tissue
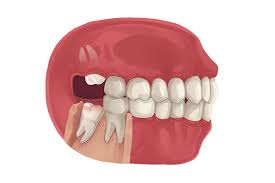
But an astounding new discovery has found that this third set of molars contain a unique form of human stem cell that can be harvested and used to regrow bone, heart tissue, and even neurons.
It's an exciting field full of promise, full of potential benefits, but substantial amounts of further research and evidence is needed to truly understand what these four extra teeth could do for us in the long term beyond tearing up almonds and salad.
For starters, wisdom teeth contain a soft center of tissue called dental pulp that keeps the tooth alive. This pulp contains immature cells which a team of scientists at the University of the Basque Country in Spain have transformed into several different kinds of cells.
Dr. Gaskon Ibarretxe, an associate professor in the Cell Biology and Histology Department at the university, led a recent study that turned pulp cells into electrically excitable pseudo-neurons that demonstrated "essentially electrical activity" in concert with proper neurons.
They could help treat damaged brain circuitry from any number of conditions or trauma.
According to Earth.com, pulp-derived stem cells have some interesting and unique properties, including the capacity to build mineralized tissue faster than bone marrow-derived stem cells. Scientists have used dental?pulp secretions to improve heart ejection fractions in mice with heart failure, and in vitro, these cells seem to lay down layers of collagen and calcium in neat, orderly sheets, making them potentially attractive for joint cartilage repair.
From the logistics and cost standpoint, they're an ideal source of stem cells. Bone marrow cells require painful injections that sometimes can't involve anesthesia, while embryonic or placental stem cells without ethical concerns require someone to decide to have a baby.
By contrast, almost all humans are born with wisdom teeth, and they're often removed in the teenage years when little DNA damage has taken place inside the dental pulp; making them exceptionally malleable and safer.
Earth.com claims 10 million wisdom teeth are removed every year, but the process of sending them to a biobank could be very simple. A kit—offered by a company like Stemodontics—could be bought and shipped to a dentist's office ahead of the procedure. The tooth is put in a vial, placed on dry ice, and rushed to a lab where the pulp would be extracted and preserved as a potentially life-changing form of cellular insurance.



