
Breaking News
 NonConformist Series: Practical Wealth - Join us virtually Dec 29-30, 2025
NonConformist Series: Practical Wealth - Join us virtually Dec 29-30, 2025
 New bill would allow private citizens to fight cartels: 'WE ARE UNDER ATTACK'
New bill would allow private citizens to fight cartels: 'WE ARE UNDER ATTACK'
 Carnivore Got Me 90% There. This One Drink Changed Everything
Carnivore Got Me 90% There. This One Drink Changed Everything
Top Tech News
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Prematurely born lambs kept alive in artificial external placenta...
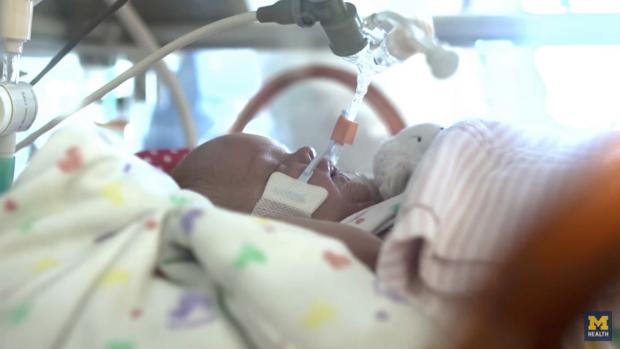
When babies are born extremely prematurely – before 24 weeks of development in the womb – their lungs aren't strong enough to provide their organs with the oxygen needed to develop properly. Nor are they strong enough to handle artificial ventilation. The result can mean a brief life for these tiniest of babies. A new artificial placenta that mimics conditions in the womb being developed by researchers at the University of Michigan (UM) might provide new hope.
The university has just reported that such an external placenta has kept five extremely premature lambs alive for a week. Although clinical trials are yet to be scheduled for humans, the researchers are hopeful that the technology might one day become a viable way to keep the earliest born babies alive until they can develop on their own.
"We thought, 'Why don't we solve the problem of prematurity by re-creating the intrauterine environment?'" says principal investigator George Mychaliska, the director of UM Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment Center. "Maybe we should treat this tiny baby like a fetus. Maybe we should treat these babies as if they are still in the womb. This is a complete paradigm shift. Our research is still in a very preliminary stage, but we've passed a significant milestone that gives us promise of revolutionizing the treatment of prematurity."

 Aluminum Causes Brain Damage
Aluminum Causes Brain Damage Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2

